Describe the Components and Structure of a Dna Nucleotide
They are mentioned as illustrations of different principles. Either A T C or G.
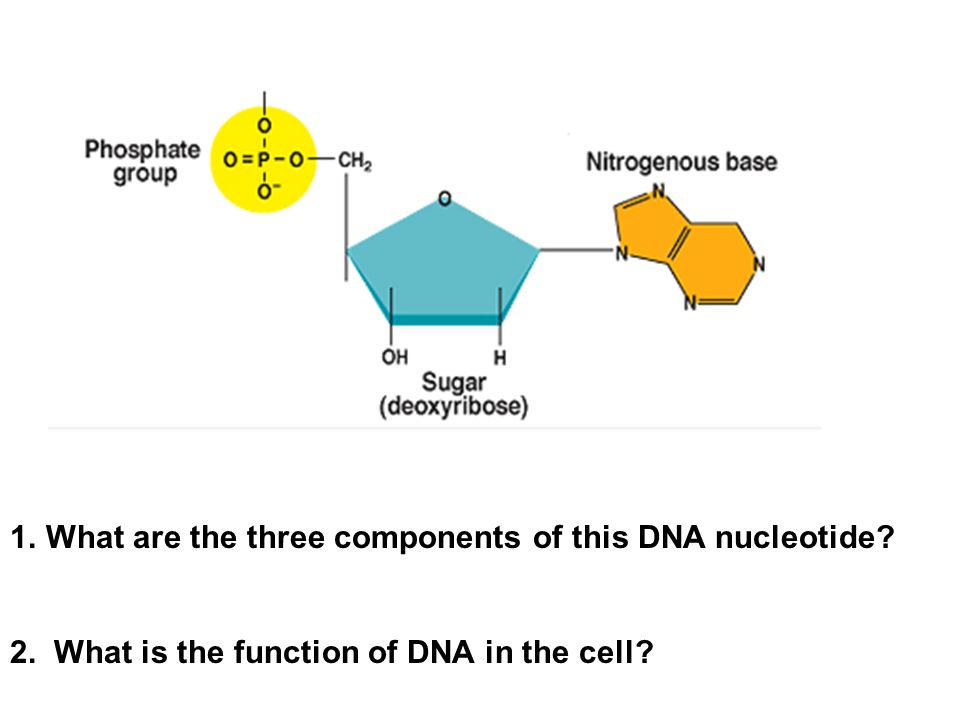
1 What Are The Three Components Of This Dna Nucleotide 2 What Is The Function Of Dna In The Cell Ppt Download
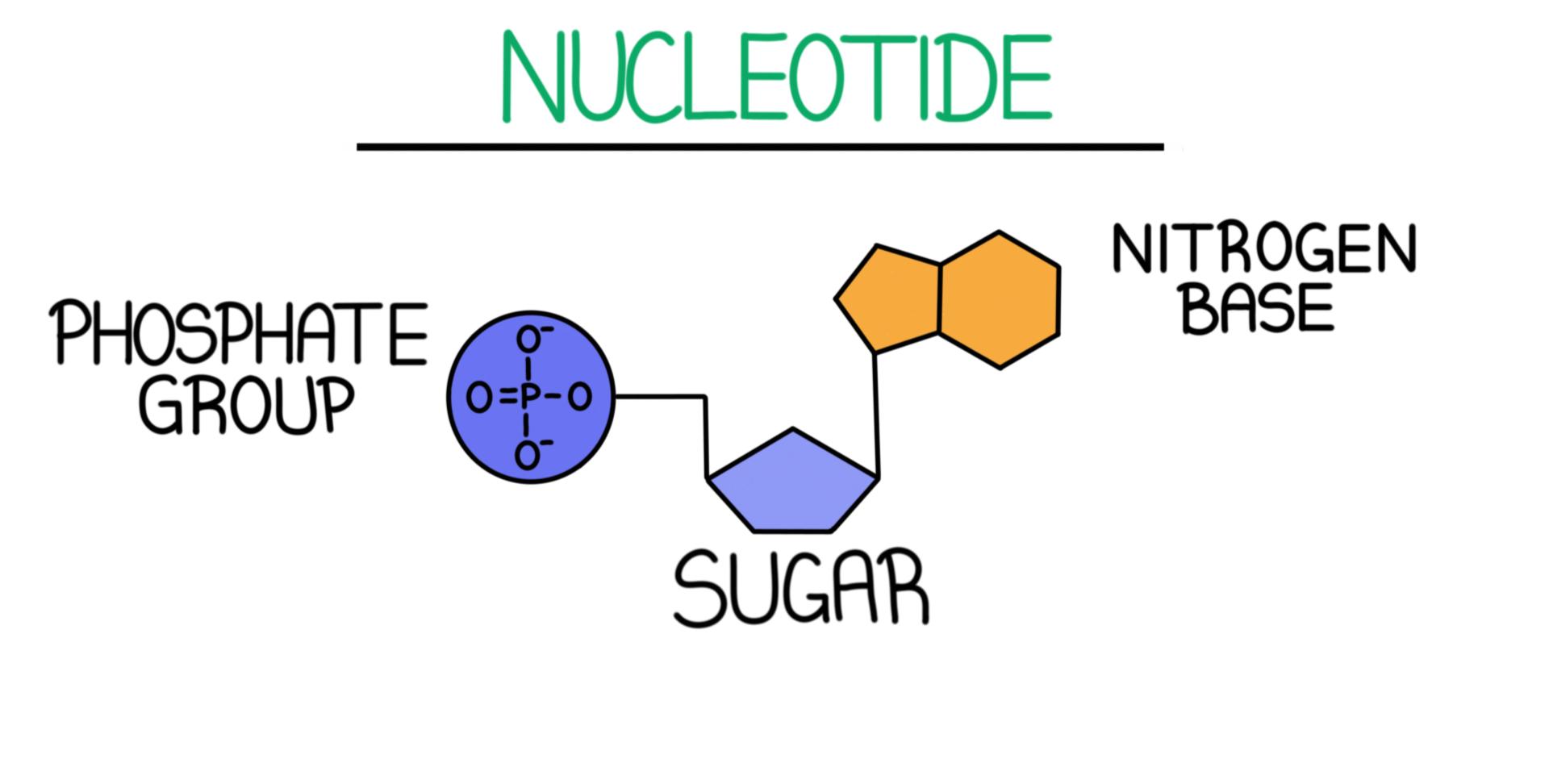
A nitrogenous base a pentose sugar and one or more phosphate groups.
. In this chapter we will discuss a fourth class of macromolecules. A nucleotide sequence that is complementary to a sequence ofmessenger RNA mRNA. The structure of DNA is dynamic along its length being capable of coiling into tight loops and other shapes.
Discuss bacterial structure and the function of the different bacterial components 4. In the 1950s Francis Crick and James Watson worked together at the University of Cambridge England to determine the structure of DNA. The structure of the chloroplast and photosynthetic.
Describe how eukaryotic and prokaryotic DNA is arranged in the cell. Identify the base pairs used in the synthesis of deoxyribonucleotides. Describe the role that chlorophylls and the other pigments found in chloroplasts play to.
Describe how the pigments found on thylakoid membranes are organized into photosystems and how they relate to photon light energy. The information in RNA although copied into another chemical form is still written in essentially the same language as it is in DNAthe. DNA Replication Models.
Discuss the distinguishing characteristics of Gram positive and Gram negative bacteria. DNA is negatively charged owing to the presence of phosphate. Describe the biochemical structure of deoxyribonucleotides.
For this lecture you should focus on the major concepts and not on the names of the different bacteria. Pauling had discovered the. Proteins lipids and carbohydrates.
Describe the different types of bacteria 3. There exist hydrogen bonds between the helices while the bases are contained in bundles within the helix. In human cells both normal metabolic activities and environmental factors such as radiation can cause DNA damage resulting in tens of thousands of individual molecular lesions per cell per day.
When antisense DNA or RNA is added to a cell it binds to a specific mRNA molecule and inactivates it by physically blocking the ability of ribosomes to move along the messenger RNA or by simply accelerating its degradation. Describe the nature of light and how it is associated with the release of electrons from a photosystem. DNA consists of a double helix backbone made of two chains of polynucleotides.
Describe the process of and key components required for translation. The structure of DNA deoxyribonucleic acid is composed of nucleotidesEach contains a deoxyribose molecule a phosphate group and a nitrogen-containing base. DNA and RNA A nucleotide is made up of three components.
Predict the likely effects of mutations in DNA on protein amino acid sequence structure and function. In all species it is composed of two helical chains bound to each other by hydrogen bonds. Written and video instructions describe each step of the model-building process.
Explain why the double helix of DNA is described as antiparallel. Through building and observing this model students explore the basic structure of phosphodiester bonds base pairs the spatial relationships among the components of nucleotides in DNA and the antiparallel nature of the double helix. Compare and contrast prokaryotic and eukaryotic transcription and translation.
If DNA is a book then how is it read. Carbon residues in the pentose are numbered 1 through 5 the prime distinguishes these residues from those in the base which are numbered without using a prime notation. The first step a cell takes in reading out a needed part of its genetic instructions is to copy a particular portion of its DNA nucleotide sequencea geneinto an RNA nucleotide sequence.
This double helix consists of two DNA strands running parallel to each other. Portions of DNA Sequence Are Transcribed into RNA. Describe the structure of DNA.
Many of these lesions cause structural damage to. DNA repair is a collection of processes by which a cell identifies and corrects damage to the DNA molecules that encode its genome. Francis Crick coined the phase the Central Dogma to describe the flow of information from nucleic acid to protein.
Learn more about the DNA transcription process where DNA is converted to RNA a more portable set of instructions for. In Microbial Metabolism we discussed three classes of macromolecules. Other scientists such as Linus Pauling and Maurice Wilkins were also actively exploring this field.
DNA is a long polymer made from repeating units called nucleotides each of which is usually symbolized by a single letter. The base is attached to the 1 position of the ribose and the.

Structure And Function Of Dna Microbiology

No comments for "Describe the Components and Structure of a Dna Nucleotide"
Post a Comment